Heavyweight! Prof. Gang Zhao, the main committee member of Yinfeng Cryomedicine Specialized Committee, published another article "Advanced Cryopreservation Engineering Strategies - A Critical Step in Utilizing Stem Cell Products".
Release time:
2023-09-08
Cryopreservation is known as the technique of solidifying time, by cooling biological materials (e.g. cells, tissues and organs) to low temperatures with the addition of cryoprotectants (generally -196°C liquid nitrogen preservation), and then rewarming them to normal temperatures (37°C) in an effective manner when needed, at which time the biological samples can still be restored and maintain their activity. Biological samples (e.g., cells, tissues and organs) are valuable in a variety of advanced medical technologies such as tissue engineering, genetic development, regenerative medicine and transplantation medicine. Currently, a series of progress has been made in the cryopreservation of cells and thin tissues (ovaries, etc.), but the cryopreservation of large-scale biological samples still faces great challenges as the volume increases, the cell types increase, and the structural complexity increases.

Recently, Prof. Gang Zhao's group at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), executive director of the International Society for Cryobiology (ISC), published a review article in Cell Regeneration entitled "Advanced cryopreservation engineering strategies: the critical step to utilize stem cell products", published in Cell Regeneration. The article comprehensively reviews the background and principles of cell cryopreservation, summarizes the commonly used engineering strategies for cell cryopreservation, and proposes a synergistic ice suppression strategy.
Cryopreservation is an important technology for long-term preservation of cells, tissues, organs and other biological materials using extremely low temperatures (-80°C or -196°C). Under cryogenic conditions, chemical and biological reactions within living cells are significantly reduced or even stopped, which is the fundamental mechanism for achieving long-term preservation of various biological samples. However, the effect of cryopreservation is affected by many complex factors and is also closely related to the sample itself and external regulation.
In addition to the ice crystal damage that may occur in cryopreservation, thermal stress damage and ice crystal damage during rewarming are often fatal, which is particularly evident in large-scale sample preservation. The research team's photothermal rewarming and electromagnetic rewarming techniques based on external physical fields have made great progress in suppressing ice crystal growth and eliminating thermal stress during rewarming. Zhao Gang's group introduced magnetic nanoparticles into cryopreservation for the first time in the world and achieved remarkable results.
It was found that for small-scale biological samples such as cells and tissues, the addition of nanoparticles to the protective agent increases the warming rate under the action of magnetic field, which can inhibit recrystallization and anti-vitrification; for large-scale samples such as organs, the nanoparticles are uniformly distributed in the samples by means of perfusion, etc., and the uniform and rapid rewarming is realized by magnetic field heating, which can effectively inhibit thermal stress loss and ice crystal damage. Electromagnetic rewarming is an effective strategy for cryopreservation and has the potential to preserve biological samples at multiple scales.
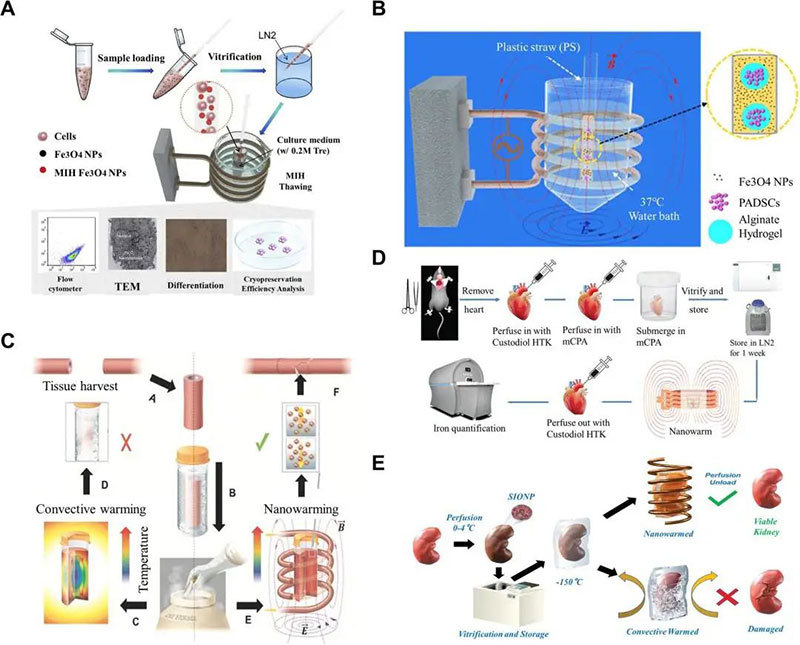
Electromagnetic rewarming of cryopreserved biological samples
In addition, various advanced hydrogel microencapsulation technologies have emerged in recent years. Microencapsulation can be used as a base technology in conjunction with other ice suppression technologies to provide multiple ice suppression effects.
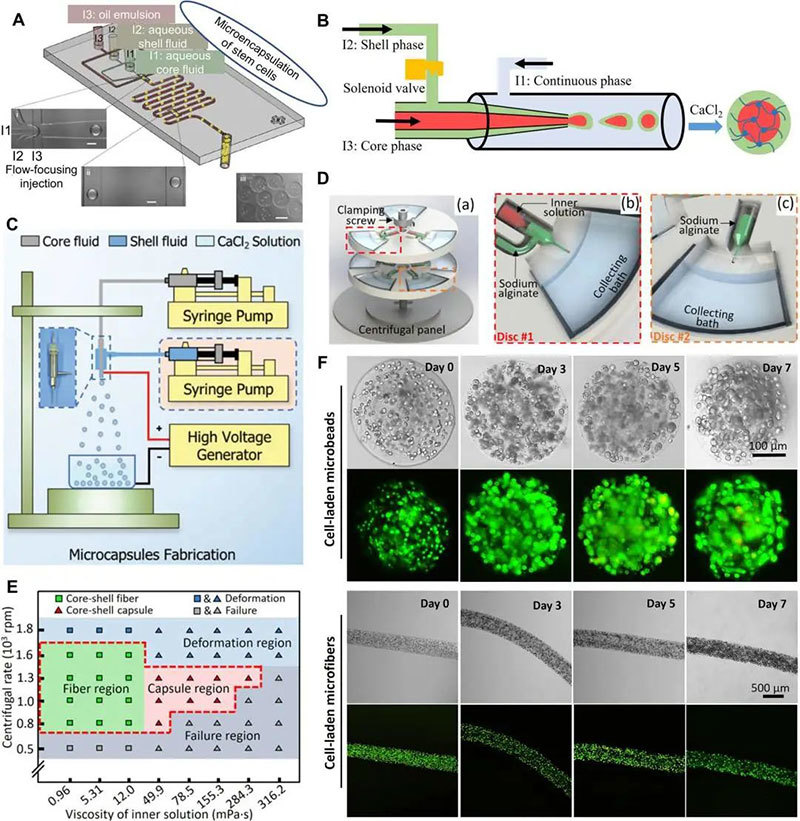
Microencapsulation/encapsulation of living cells (living cell constructs)
Based on this, Zhao Gang's team proposed the engineering strategy of synergistic ice suppression, i.e., the effective integration of two or more advanced engineering technologies into the field of cryopreservation, and the synergistic effect in the cooling and rewarming process to realize the high-quality preservation of biological samples.
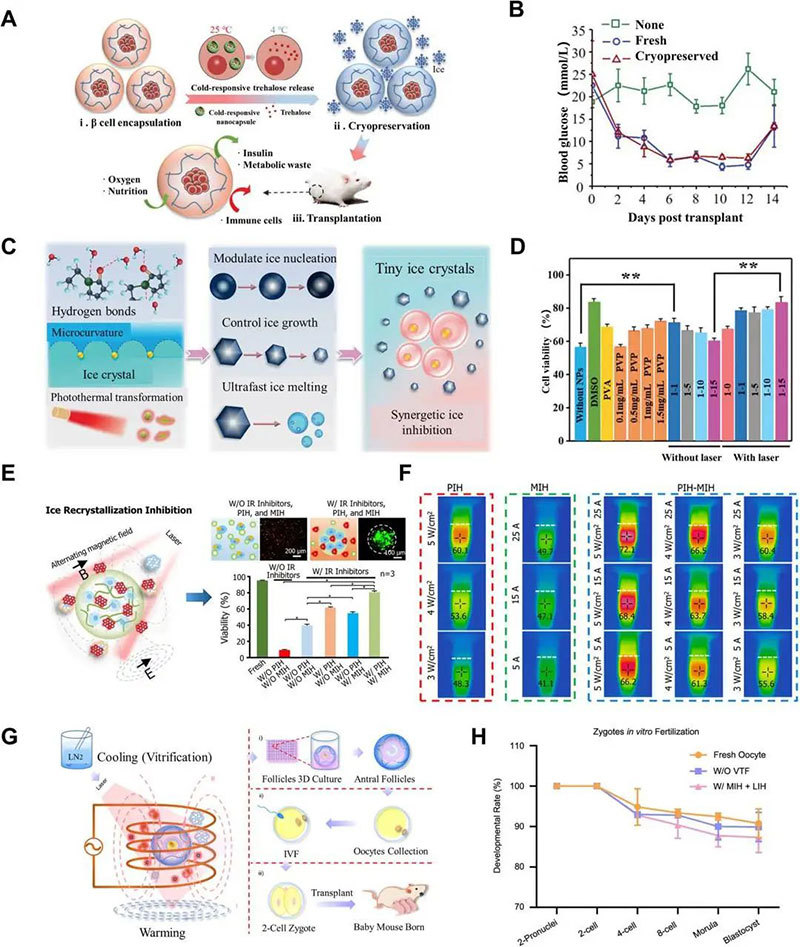
coordinated ice suppression
The formation and growth of ice crystals and the damage they cause have long been one of the major challenges to the deep cryopreservation of natural living materials such as living cells, tissues and organs, as well as biocomposites such as living cellular constructs and cultures. In-depth understanding of the mechanism of ice crystal formation and the development of efficient methods or technologies to effectively regulate the formation of ice crystals during cryogenic freezing and rewarming and thawing processes are of great value for basic research and practical applications.
The article elaborates that functional nanomaterials are the research hotspot of ice suppression materials. However, most of the existing studies only focus on the molecular ice suppression effect of nanomaterials, and there are not many studies on their synergistic ice suppression effect (e.g., molecular ice suppression effect combined with photothermal or magnetothermal effect, etc.), which leads to the proposal of a series of advanced engineered ice suppression technologies, including photothermal, magnetothermal rewarming, cell encapsulation and synergistic ice suppression.
Shandong Yinfeng Life Science Research Institute, established in 2015, has been taking cryogenic biomedical research and cryopreservation as an important subject task, focusing on the development of a variety of cryoprotectants, cryogenic equipment development, tissue and organ cryopreservation research, etc., especially for the existence of common problems in the deep cryopreservation of tissues and organs at large scales, and the international and domestic experts and scholars in the fields of cryogenic biomedicine, clinical medicine, etc., to We will establish a cooperation platform for information and result sharing and technology opening to strengthen scientific research exchanges and give full play to the advantages of all parties. We believe that with the joint promotion of all of us, the cryopreservation engineering strategies and results of cells, tissues and organs will come out one after another, bringing a prosperous future for regenerative medicine.
Latest developments
Over the two days, the symposium was not only a collision of ideas but also seeds sown to advance social progress in life culture. The Shandong Yinfeng Life Science Public Welfare Foundation will continue to use technology as wings and culture as roots, collaborating with all sectors of society to enhance the quality of life for the Chinese people and build a human-centered life care system.
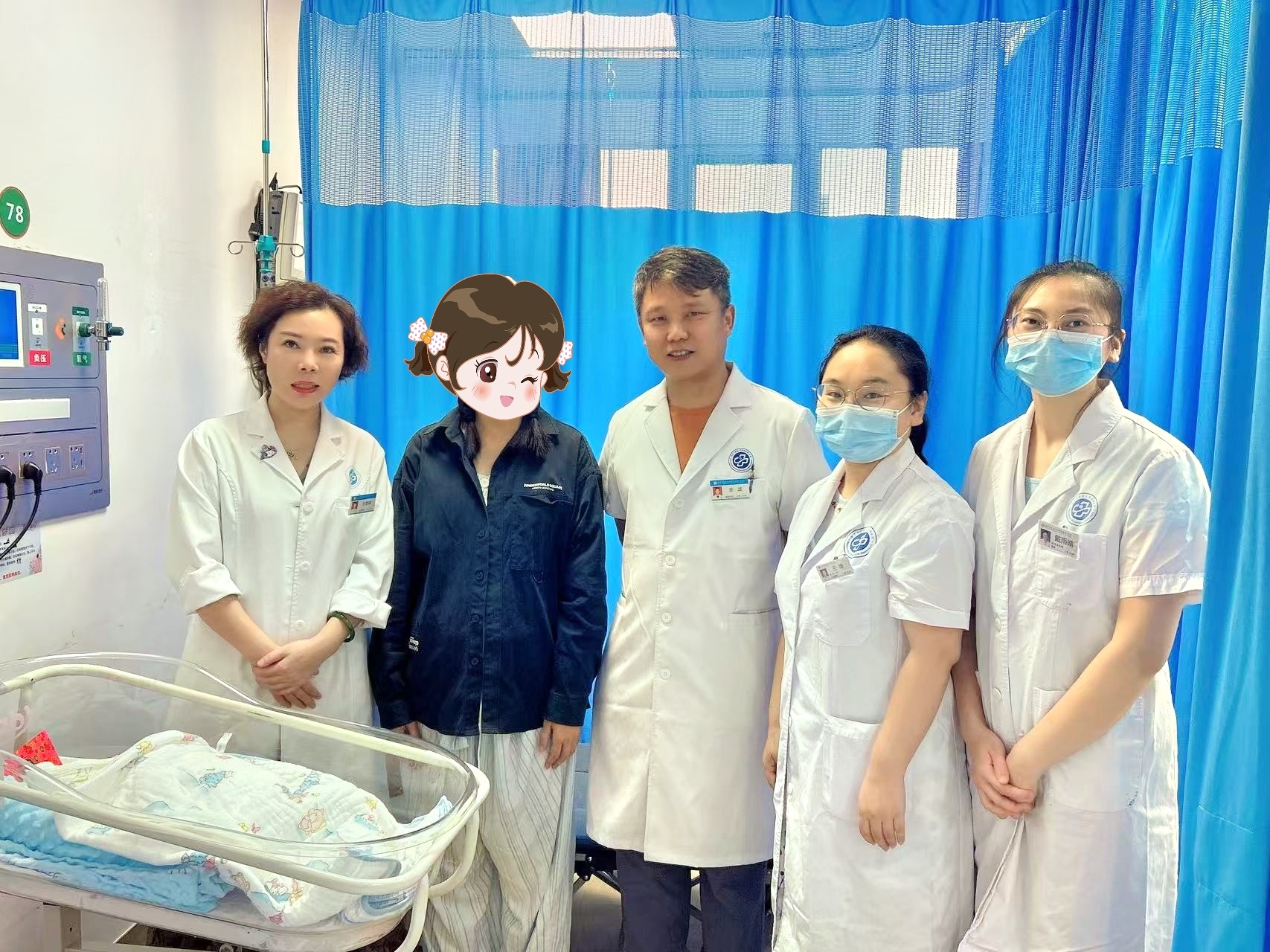
According to recent announcements by the Jinan Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology, 11 outstanding achievements from Jinan have been included in the 2025 "Shandong Outstanding Achievements Report" project. Among them is the globally first-of-its-kind ovarian tissue dual-activation technology developed by Shandong Silver Med Life Science Research Institute (Jinan).
Recently, Frigid Zone Medicine, an authoritative international journal in the field of cryomedicine, published an important review titled "Advances in the Detection Methods for Assessing the Viability of Cryopreserved Samples". Written by the team of Yinfeng Cryomedical Research Center, the article systematically reviews and analyzes various detection techniques currently used to evaluate the viability of cryopreserved cells, tissues, and organs. It also proposes key directions from the perspectives of methodological integration and future instrument development, offering crucial theoretical support and practical guidance for the long - term cryopreservation of complex tissues and organs.
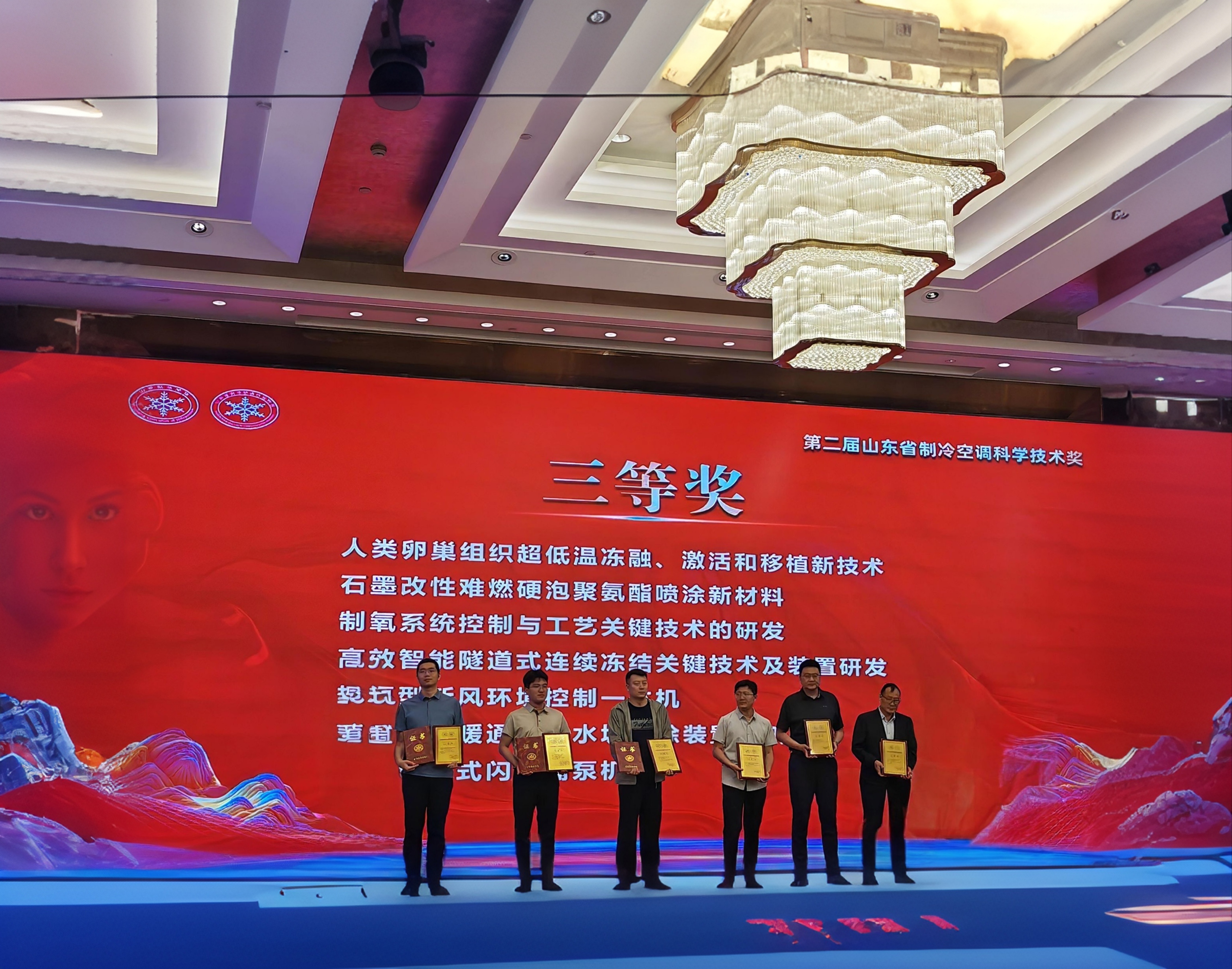
Recently, the "Novel Technology for Ultra-Low Temperature Cryopreservation, Activation, and Transplantation of Human Ovarian Tissue," developed through a collaborative effort between Shandong Yinfeng Life Science Research Institute and Beijing University of Chinese Medicine Shenzhen Hospital, has been awarded the 2025 Shandong Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Science and Technology Award. This groundbreaking technology pioneers a new pathway for female fertility preservation, marking a significant leap in China’s interdisciplinary advancements in reproductive medicine and cryobiology.
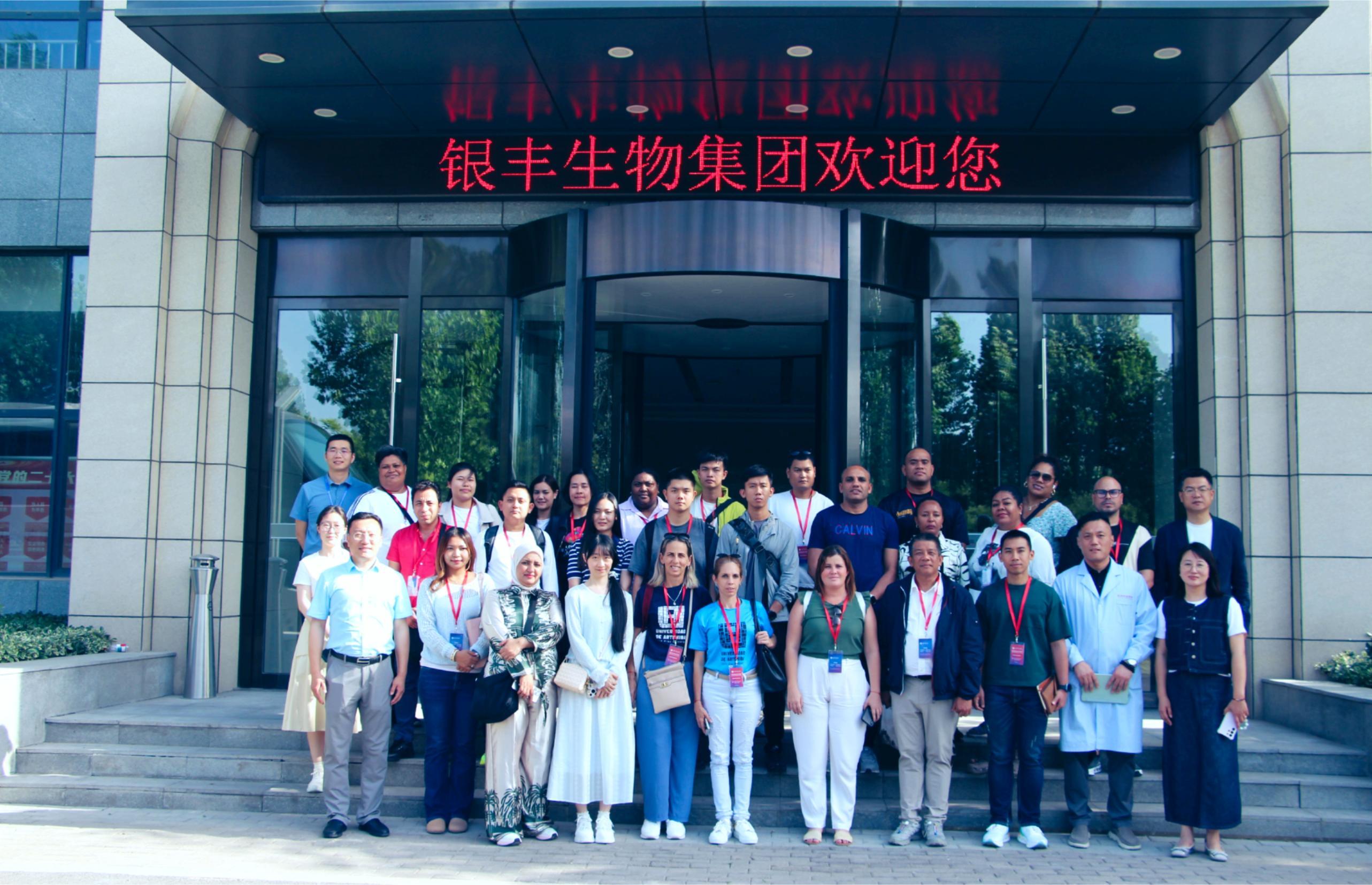
On May 19, a delegation from the Chinese Training Workshop for Government Officials of Developing Countries visited the exhibition hall of Yinfeng Biological Group's Cryomedicine Research Center. Government officials from multiple countries gained in-depth insights into Yinfeng’s innovative achievements in cryobiomedicine, cell storage, genetic technology, and other fields. They engaged in discussions with the delegation on technology transfer and international cooperation, contributing to the building of a global community with a shared future for humanity.