The 2024 World's Top Ten Scientific and Technological Advances Announced, with Significant Achievements in Life Sciences
Release time:
2025-02-07
Recently, the "2024 China/World Top Ten Scientific and Technological Advances" organized by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Engineering was unveiled. In the list of the world's top ten scientific advancements, breakthroughs in cell and gene technologies stood out, including the first 3D-printed functional human brain tissue, CAR-T therapy, gene editing, Google's new quantum chip, super microscope, and more.
Scientists First 3D-Print Functional Human Brain Tissue
American scientists have succeeded in the first 3D printing of functional human brain tissue, which can grow and function like traditional brain tissue. Researchers used a horizontal layering scheme to place brain cells cultured from induced pluripotent stem cells into a soft "bio-ink" gel, ultimately cultivating neurons. The printed cells form connections within and between each printed layer through the medium, creating a network comparable to a human brain.
This 3D printing technology does not require special bioprinting equipment or cultivation methods to maintain tissue health and can be studied using microscopes, standard imaging techniques, and electrodes. Scientists believe this breakthrough is significant for researching the brain and treating various neurological and neurodevelopmental diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Google's New Quantum Chip Surpasses Precision Milestone
Google's Willow quantum chip, developed in the United States, has achieved "below threshold" quantum computation, marking an important milestone in the quest to create practical quantum computers with sufficient precision.
Willow is an improved version of this technology, larger in scale with 105 physical qubits. According to Google Quantum Computing's head, Willow is powerful enough to complete a random circuit sampling task in about 5 minutes that the world's largest supercomputer is estimated to take 1,025 years to complete.
First "Map of the Universe"
The Euclid space telescope has released its first scientific results, including the first "map of the universe" image. The European Space Agency (ESA) announced these results, revealing a group of scientific images showcasing shining galaxy clusters, nearby spiral galaxies, and colorful interstellar gas clouds nurturing hundreds of thousands of young stars. The space telescope captured over 14 million galaxies in a stitched image, demonstrating for the first time a "map of the universe," enhancing understanding of the roles of dark matter and dark energy in cosmic structure. This massive image, composed of 260 frames, is the first display of the largest and most precise map of the universe ever created by the Euclid space telescope.
Over the next six years, the Euclid space telescope will automatically scan about one-third of the night sky. Researchers anticipate the final map will reveal around 8 billion galaxies, each containing billions of stars, covering 10 billion years of cosmic history.
Scientists Map the Largest Brain Gene Regulatory Network
In May 2024, researchers published 15 papers in the journals Science, Science Advances, and Scientific Reports, claiming they have mapped the largest and most advanced multi-dimensional brain gene regulatory network to date. These papers report the findings on several key themes, extending previous discoveries and exploring multiple cortical and subcortical regions of the human brain. These brain areas play crucial roles in a range of important functions, including decision-making, memory, learning, emotion, reward processing, and motor control.
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and used post-mortem brain tissue from over 2,500 donors to map gene regulatory networks across different stages of brain development and associated with various brain diseases.
Highly Accurate 3D Atlas of Cancer Cells Emerges
In October 2024, the Human Tumor Atlas Network (HTAN) researchers, through a series of 12 papers published in Nature, drew an ultra-precise 3D atlas of tumor cells by analyzing hundreds of thousands of cells from human and animal tissues. They also created a "molecular clock" to track cellular changes leading to cancer.
Scientists analyzed cell tissues from 131 samples of six types of cancers and used the "molecular clock" to track how normal cells become dysfunctional and proliferate within the gut. Using single-cell analysis and the CRISPR gene-editing tool, mutations were generated in each cell's DNA to record the timeline of each cell's changes and divisions. This approach was applied to 418 human colon polyps, revealing that up to 30% of the polyps originated from several cell types. These findings challenge the idea that colon cancer originates from a single rogue cell in the intestinal lining and could provide more opportunities for early diagnosis and intervention.
First Bilingual Brain-Reading Device Enables Speech for Aphasia Patients
A study published in Nature Biomedical Engineering by American researchers shows that an artificial intelligence (AI) system coupled with a brain implant has helped a person who could not speak normally to communicate in two languages for the first time.
The study found that much brain activity related to Spanish and English comes from the same area, providing insights into how the brain processes language and offering hope for restoring multilingual capabilities in individuals unable to communicate verbally.
SpaceX's Starship Successfully Recovers Booster with "Chopsticks" During the Fifth Test Flight
In October 2024, SpaceX's next-generation heavy-lift rocket, Starship, conducted its fifth test flight. The booster was "caught" mid-air by mechanical arms referred to as "chopsticks" on the launch tower during landing, marking the first time mid-air capture recovery was achieved. The spacecraft splashed down in the Indian Ocean. The booster recovery method using mechanical arms facilitates faster recovery and reuse, increasing the Starship's launch frequency.
The Starship rocket measures about 120 meters in length and approximately 9 meters in diameter, consisting of two parts: the approximately 70-meter-long "Super Heavy" booster as the first stage and the Starship spacecraft as the second stage, both of which are reusable. The rocket is designed to transport humans and cargo to Earth's orbit, the moon, and even Mars.
World's First Stem Cell Treatment to Restore Human Vision
A Japanese research team achieved the world's first corneal transplant surgery using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). In four patients with severely impaired vision, three experienced significant vision improvement lasting over a year after receiving stem cell transplants, while another patient saw temporary improvement.
Researchers extracted blood cells from a healthy donor and reprogrammed them to an embryonic-like state, converting them into a thin, transparent pebbled corneal epithelial cell layer. As part of the surgery, the team removed scar tissue covering the cornea of one eye of the patient, then sutured the donor epithelial cells in place, covering them with a soft, protective contact lens. The team plans to initiate clinical trials in March 2025 to further assess the efficacy of this approach.
First Ever Human Transplantation of a Genetically Edited Pig Kidney Completed
In March 2024, a surgical team at Massachusetts General Hospital completed the world's first live human kidney transplant from a pig. The transplant procedure was granted "compassionate use" approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The kidney used in this transplant was obtained from a miniature pig whose genome had been edited, modifying 69 genetic factors. These modified genomes were designed to prevent organ rejection and reduce the risk of virus transmission to the recipient.
The initial success of the world's first live human kidney transplant from a pig has sparked hope among researchers for larger-scale clinical trials involving pig organs. Such trials could potentially bring xenotransplantation into clinical practice.
Long-lasting HIV Preventive Injection Trial Succeeds
In June 2024, American biopharmaceutical company Gilead announced that its beanereline caps IDbudex inhibitor, "Lenacapavir," administered twice annually, showed 100% efficacy in preventing HIV. A study published in Science credited the drug's success to a breakthrough in basic research, unveiling a new understanding of the structure and function of the HIV capsid protein it targets. Given that many viruses have their own capsid proteins, the successful application of Lenacapavir implies that similar capsid inhibitors could potentially combat other viral diseases.
Regulatory approval for Lenacapavir is expected no sooner than mid-2025, with its price yet to be disclosed, leaving the possibility of accelerating the end of the AIDS pandemic uncertain. American experts caution that Lenacapavir cannot replace vaccines.
This annual selection event, successfully held for 31 years, has attracted significant attention from society, further deepening the public's understanding of domestic and international technological development trends, and playing a positive role in spreading knowledge of frontier technologies. It has also reignited interest and discussion in life sciences and provided a comprehensive platform for showcasing global technological innovation.
Latest developments
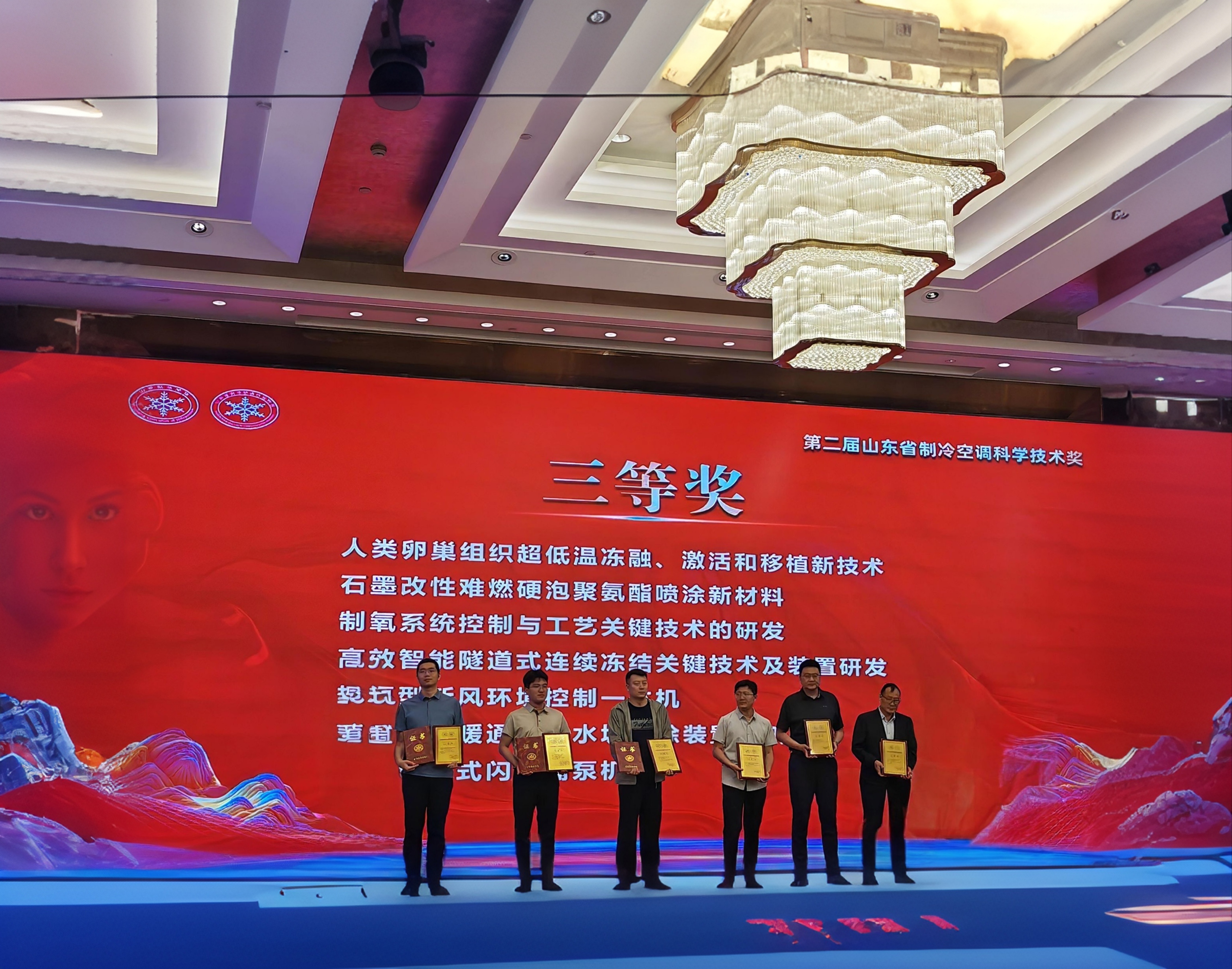
Recently, the "Novel Technology for Ultra-Low Temperature Cryopreservation, Activation, and Transplantation of Human Ovarian Tissue," developed through a collaborative effort between Shandong Yinfeng Life Science Research Institute and Beijing University of Chinese Medicine Shenzhen Hospital, has been awarded the 2025 Shandong Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Science and Technology Award. This groundbreaking technology pioneers a new pathway for female fertility preservation, marking a significant leap in China’s interdisciplinary advancements in reproductive medicine and cryobiology.
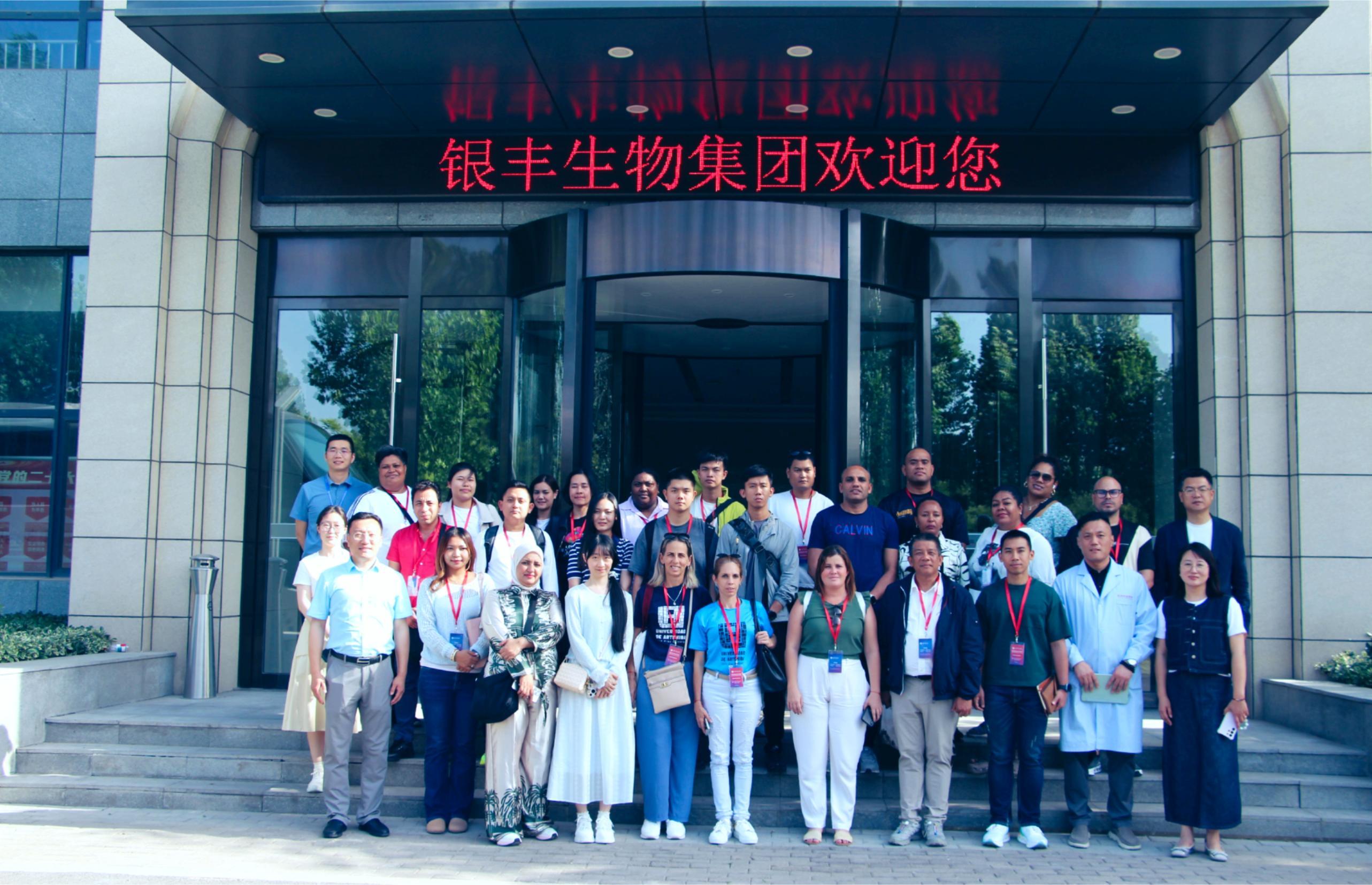
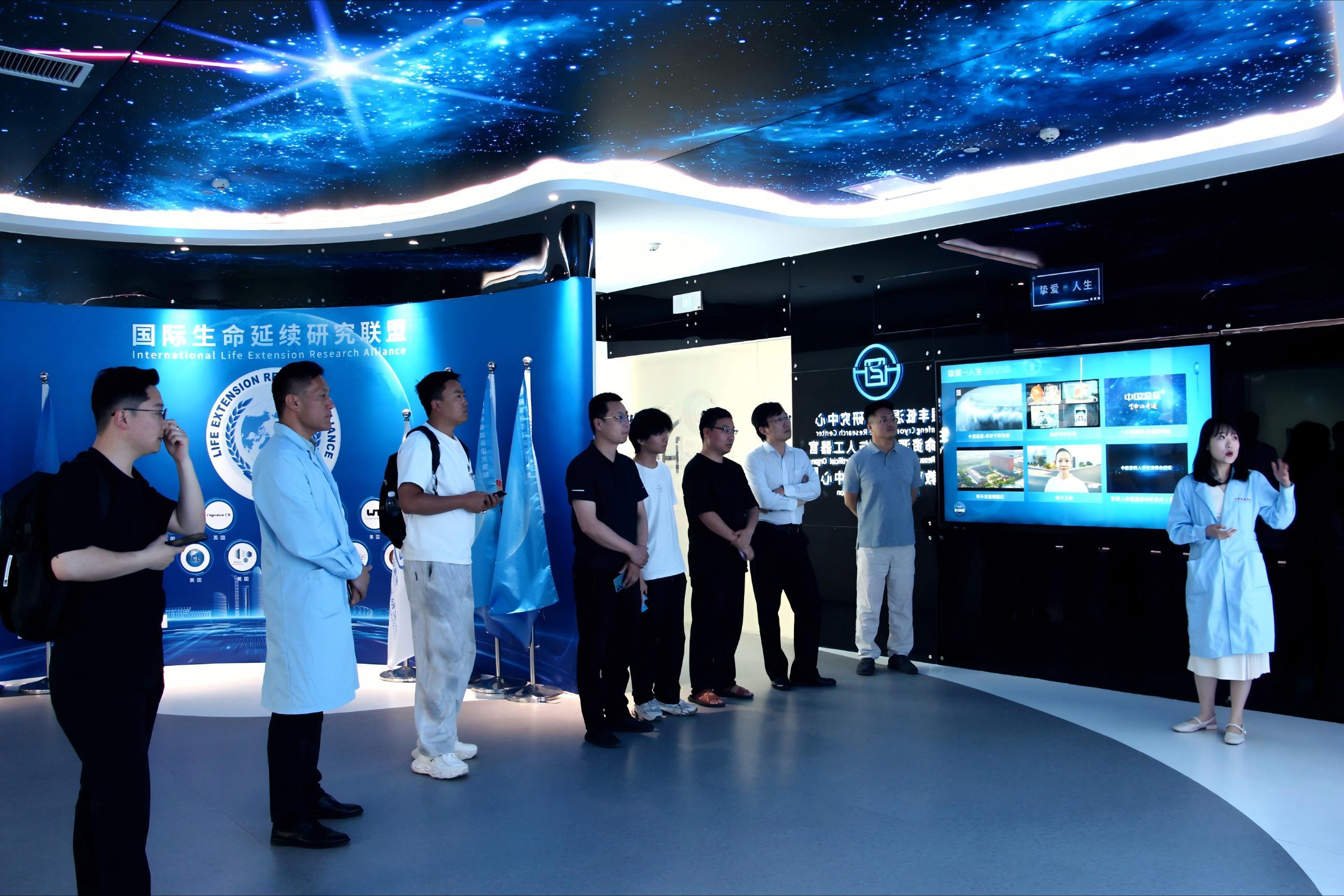
On May 19, a delegation from the Chinese Training Workshop for Government Officials of Developing Countries visited the exhibition hall of Yinfeng Biological Group's Cryomedicine Research Center. Government officials from multiple countries gained in-depth insights into Yinfeng’s innovative achievements in cryobiomedicine, cell storage, genetic technology, and other fields. They engaged in discussions with the delegation on technology transfer and international cooperation, contributing to the building of a global community with a shared future for humanity.
On the morning of May 17, 2025, an immersive exploration into life sciences and cryomedicine concluded successfully at Jinan Yinfeng Biological Science Park. Hosted by the Shandong Yinfeng Life Science Research Institute, this event offered members a firsthand look into the research base through activities such as ultra-low temperature cryotherapy experiences, brainwave signal acquisition system trials, and expert panel discussions. Participants witnessed the infinite possibilities that cryogenic technology and life sciences hold for humanity.
The international academic platform ScholarGPS recently announced its global lists of Highly Ranked Scholars - Lifetime and Highly Ranked Scholars - Prior 5 Years, recognizing the top 0.05% of scholars across various disciplines. Among the selected Chinese scholars are national-level talents, leading figures in specialized fields, and seasoned academics dedicated to long-term research.
In January 2025, members of the Yinfeng cryomedicine team actively participated in the "Sino-French Aerial Emergency Medical Rescue Training" and obtained certification. This signifies a further enhancement of the team's professional capabilities in the field of international emergency medical rescue.