A world first! Corneal autotransplantation successfully restores sight to blind man
Release time:
2023-04-10
Corneal disease is one of the major blinding eye diseases in the world today, and corneal transplantation is the most effective method to remove blindness and restore vision.

At present, corneal transplantation materials are in short supply and materials are unevenly distributed in various regions. Clinically, corneal transplantation often cannot meet the needs of large numbers of patients and emergency operations. Therefore, the preservation of limited transplantation materials has attracted increasing attention.
According to a report by Science and Technology Daily on March 29, Indian media wionews reported on the 27th that in the world's first corneal autotransplantation operation, an Italian doctor transplanted the entire ocular surface of the left eye of an eighty-year-old man who was blind, including the cornea and the entire conjunctiva. and part of the sclera was transplanted into the blind right eye, restoring vision in his right eye.
The four-hour transplant operation was performed about two weeks ago at the Molinete Hospital in Turin, Italy, by Michele Rebaldi, director of the Molinete University Eye Clinic, and Vincenzo Sarni, a cornea transplant specialist. Cora took charge. The patient, Emiliano Bosca, can now see and identify people and objects around him and can move around without help. For aesthetic reasons, doctors reconstructed his left eye using donated tissue.
Boska said that now he can see the time on the phone, the outline of objects, and the colors of cars passing by on the street. "I feel as if I have been reborn."
Doctors noted that the surgery on the right eye was successful because it was reconstructed with the patient's own tissue, making it less likely to suffer from rejection problems common in previous transplant surgeries. The technology could be applied to other patients with conditions similar to Boska's.
Since the first report on the success of human penetrating corneal transplantation, corneal transplantation technology has developed rapidly. However, due to the limited number of fresh donor grafts, it often cannot meet clinical needs. Therefore, the preservation and requirements of transplantation materials have attracted increasing attention. Commonly used Preservation methods include wet room preservation, organ culture preservation, and vacuum freeze-drying. However, the above preservation methods are prone to short preservation times and are difficult to achieve the scientific requirements of modern eye banks that require donors to be screened for HLA matching, HIV, and hepatitis infectious diseases. Requirements may easily lead to surgical failure and increase the chance of transplant infection.
Yinfeng Research Institute is committed to the cryopreservation of complex tissues and organs to protect human life and health. The cryopreservation method is the ultimate solution to the long-term preservation of donor corneas and promotes the development of corneal transplantation. Although this method has shortcomings such as complex equipment and high technical requirements for operation, its application value is beyond doubt. Through in-depth research on the selection of cryoprotective agents for cryopreservation, improvement of cooling and rewarming rates, whether there is apoptosis and the generation of oxygen free radicals during the preservation process, the clinical application of cryopreservation has been Applications will surely be further optimized and expanded.
Next article
Latest developments
Over the two days, the symposium was not only a collision of ideas but also seeds sown to advance social progress in life culture. The Shandong Yinfeng Life Science Public Welfare Foundation will continue to use technology as wings and culture as roots, collaborating with all sectors of society to enhance the quality of life for the Chinese people and build a human-centered life care system.
According to recent announcements by the Jinan Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology, 11 outstanding achievements from Jinan have been included in the 2025 "Shandong Outstanding Achievements Report" project. Among them is the globally first-of-its-kind ovarian tissue dual-activation technology developed by Shandong Silver Med Life Science Research Institute (Jinan).
Recently, Frigid Zone Medicine, an authoritative international journal in the field of cryomedicine, published an important review titled "Advances in the Detection Methods for Assessing the Viability of Cryopreserved Samples". Written by the team of Yinfeng Cryomedical Research Center, the article systematically reviews and analyzes various detection techniques currently used to evaluate the viability of cryopreserved cells, tissues, and organs. It also proposes key directions from the perspectives of methodological integration and future instrument development, offering crucial theoretical support and practical guidance for the long - term cryopreservation of complex tissues and organs.
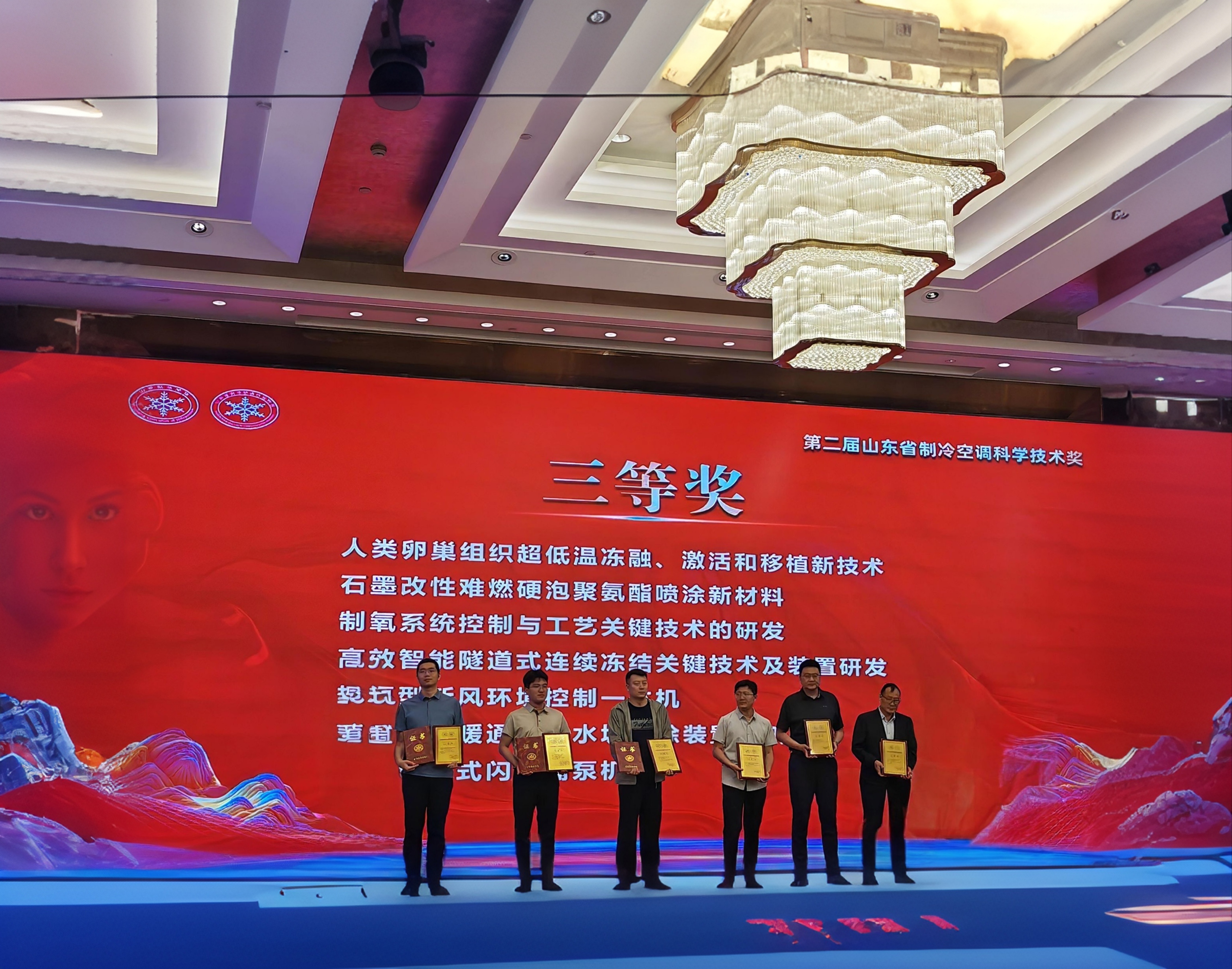
Recently, the "Novel Technology for Ultra-Low Temperature Cryopreservation, Activation, and Transplantation of Human Ovarian Tissue," developed through a collaborative effort between Shandong Yinfeng Life Science Research Institute and Beijing University of Chinese Medicine Shenzhen Hospital, has been awarded the 2025 Shandong Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Science and Technology Award. This groundbreaking technology pioneers a new pathway for female fertility preservation, marking a significant leap in China’s interdisciplinary advancements in reproductive medicine and cryobiology.
On May 19, a delegation from the Chinese Training Workshop for Government Officials of Developing Countries visited the exhibition hall of Yinfeng Biological Group's Cryomedicine Research Center. Government officials from multiple countries gained in-depth insights into Yinfeng’s innovative achievements in cryobiomedicine, cell storage, genetic technology, and other fields. They engaged in discussions with the delegation on technology transfer and international cooperation, contributing to the building of a global community with a shared future for humanity.